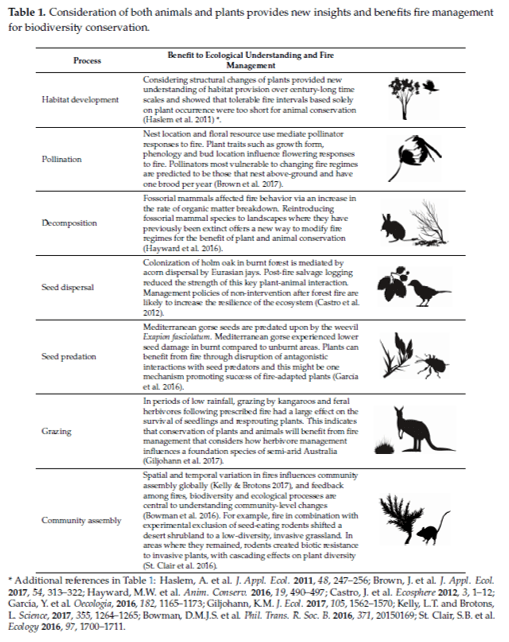
We call for better integration of animal-based and plant-based approaches in fire ecology (summarised in the figure below).
This one was a few years in the making but was a lot of fun to write with a team of scientists doing novel research, on a range of taxa, in ecosystems around the world.
The paper is open access and you can download the whole thing here.
Abstract. Conserving animals and plants in fire-prone landscapes requires evidence of how fires affect modified ecosystems. Despite progress on this front, fire ecology is restricted by a dissonance between two dominant paradigms: ‘fire mosaics’ and ‘functional types’. The fire mosaic paradigm focuses on animal responses to fire events and spatial variation, whereas the functional type paradigm focuses on plant responses to recurrent fires and temporal variation. Fire management for biodiversity conservation requires input from each paradigm because animals and plants are interdependent and influenced by spatial and temporal dimensions of fire regimes. We propose that better integration of animal-based and plant-based approaches can be achieved by identifying common metrics that describe changes in multiple taxa; linking multiple components of the fire regime with animal and plant data; understanding plant-animal interactions; and incorporating spatial and temporal characteristics of fires into conservation management. Our vision for a more integrated fire ecology could be implemented via a collaborative and global network of research and monitoring sites, where measures of animals and plants are linked to real-time data on fire regimes.